Sure! Here's the article on the theme of "What is a DC Gearmotor?" divided into two parts, each containing 700 words, as you requested.
What is a DC Gearmotor?
In the world of mechanical and electrical engineering, efficiency and precision are key factors in designing functional systems. When it comes to powering small devices with high torque, one of the most reliable solutions is a DC gearmotor. But what exactly is a DC gearmotor, and why are they so popular in industries ranging from robotics to automotive?
A DC gearmotor is a type of electric motor that integrates a direct current (DC) motor with a gearbox. The DC motor itself generates rotational power from electrical energy, while the gearbox modifies the speed and torque of the motor's output to suit specific requirements. This combination provides a powerful and efficient way to drive machinery with a tailored balance of speed and torque.
Components of a DC Gearmotor
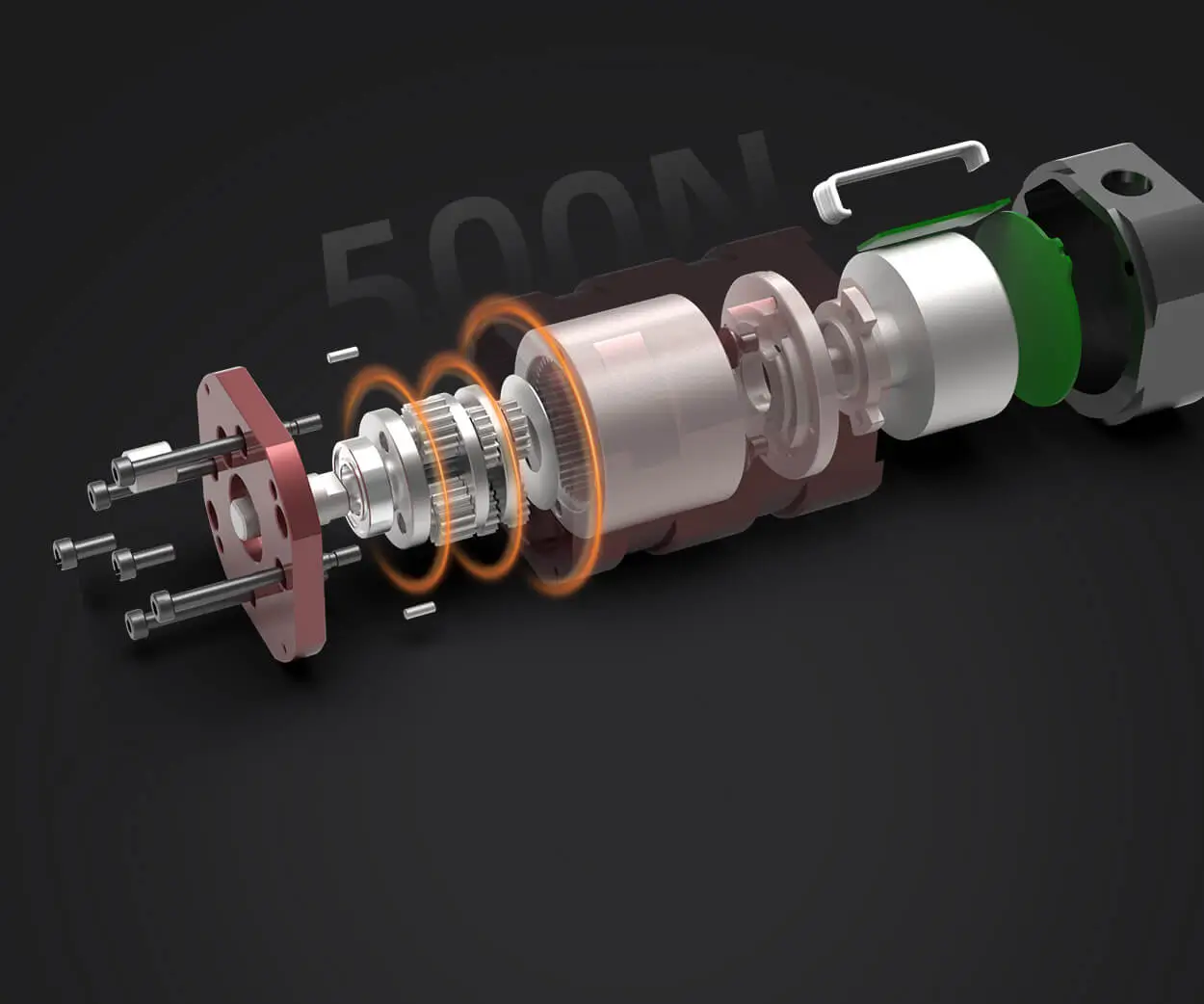
To fully appreciate how a DC gearmotor works, it's important to understand its core components:
DC Motor: The heart of a DC gearmotor is the DC motor, which converts electrical energy into mechanical energy (rotation). DC motors operate on the principle of electromagnetism, where a current is passed through a coil, generating a magnetic field that interacts with permanent magnets, causing the motor shaft to rotate.
Gearbox: The gearbox, or gear assembly, is where the magic happens. It reduces the rotational speed of the motor while simultaneously increasing the torque (rotational force). The gearbox consists of a series of gears, which work together to achieve the desired output speed and torque.
Output Shaft: The final component of the motor is the output shaft, which transmits the power from the motor to the mechanical load (e.g., wheels, conveyor belts, robotic arms).
How Does a DC Gearmotor Work?
When you power a DC gearmotor, an electrical current is supplied to the DC motor, causing it to rotate. The rotation from the motor is transferred to the gearbox, which alters the speed and torque. The speed of the rotation is typically reduced, while the torque is amplified.
To break it down further:
Speed Reduction: Gearboxes achieve speed reduction through a system of gears with different sizes. The larger the gear, the slower it turns, and the smaller the gear, the faster it turns. This difference in gear sizes allows the motor to rotate more slowly, but with greater power.
Torque Amplification: By reducing speed, the gearbox increases the torque. This allows the motor to handle heavier loads and perform tasks that would otherwise require more energy or a larger motor.
This combination makes DC gearmotors ideal for applications where you need controlled movement, consistent torque, and a reliable power source.
Advantages of DC Gearmotors
There are several reasons why DC gearmotors are used in a variety of applications. Here are some of the key advantages:
High Torque at Low Speed: One of the most notable benefits of DC gearmotors is their ability to provide high torque at lower speeds. This is crucial for tasks that require precision and force, such as in robotics, conveyor belts, and electric vehicles.
Compact and Efficient: DC gearmotors are generally compact, meaning they can be integrated into systems with limited space. Despite their small size, they are highly efficient and capable of delivering a significant amount of power relative to their size.
Adjustable Speed and Torque: The speed and torque output of a DC gearmotor can be easily adjusted by modifying the gear ratio or the input voltage, providing flexibility for various applications.
Cost-Effective: Compared to other motor options, DC gearmotors are relatively affordable, making them a cost-effective solution for many industries, especially when working on smaller-scale projects.
Applications of DC Gearmotors
DC gearmotors are found in a vast array of industries and applications. Here are just a few examples of where they play a crucial role:
Robotics: Robots, especially small and mid-sized ones, often use DC gearmotors for movement. The high torque and low speed provided by the motor are ideal for tasks like turning wheels, moving arms, or manipulating objects.
Electric Vehicles (EVs): DC gearmotors are used in EVs to power the wheels. Their ability to provide a balanced mix of speed and torque makes them ideal for moving vehicles, especially in low-speed, high-torque situations.
Automated Machinery: Many industrial machines, such as conveyor belts, packaging systems, and assembly lines, use DC gearmotors to operate efficiently.
Household Appliances: From washing machines to electric fans, DC gearmotors help power the movement of parts in various household appliances, providing smooth and consistent operation.
Toys and Gadgets: Many battery-powered toys and gadgets, including remote-controlled cars and drones, rely on DC gearmotors to move and operate.
Choosing the Right DC Gearmotor for Your Application
When selecting a DC gearmotor for a particular application, there are several key factors to consider to ensure the motor fits your needs. Below are some of the primary considerations:
Voltage and Current Requirements: DC gearmotors come in various voltage ratings, typically ranging from 3V to 24V, or even higher for industrial applications. It's important to match the voltage of the gearmotor with your system’s power supply to ensure optimal performance.
Speed and Torque Needs: As discussed earlier, DC gearmotors can be configured for different speed and torque outputs based on the gear ratio and the motor design. The gear ratio should be selected depending on the desired speed and torque for your specific application. For instance, if you need a high torque at low speed (e.g., for heavy-duty machinery), you'll need a gearmotor with a higher gear ratio.
Size and Form Factor: The physical dimensions of the DC gearmotor are also crucial. If you're working in a confined space, you’ll need a motor that fits within the available room while still delivering sufficient power.
Efficiency and Power Consumption: The efficiency of the motor determines how much energy is lost as heat and how much is used for mechanical work. A more efficient motor will consume less power and run cooler, leading to longer operational life.
Durability and Lifespan: Depending on the environment in which the gearmotor will operate, durability might be an important factor. Some motors are designed for high-durability applications, while others are intended for light-duty use. Be sure to choose a gearmotor that suits the wear and tear of your intended application.
Environmental Considerations: If the gearmotor will be exposed to extreme conditions, such as high humidity, dust, or temperature variations, it’s essential to select a motor with appropriate protection ratings (e.g., IP ratings for ingress protection).
Innovations in DC Gearmotor Technology
Over the years, DC gearmotor technology has evolved significantly, leading to improvements in efficiency, power, and versatility. Some of the recent innovations include:
Brushless DC Gearmotors (BLDC): While traditional DC motors use brushes to transfer current to the armature, brushless motors eliminate these brushes, resulting in less wear and tear, higher efficiency, and longer lifespan. These are becoming increasingly popular in applications where durability and performance are critical.
Smart Gearmotors: With the rise of the Internet of Things (IoT) and automation, gearmotors are now being integrated with sensors and connectivity features. This allows for remote monitoring, real-time feedback, and even predictive maintenance, making them more intelligent and efficient.
Miniature DC Gearmotors: In applications where size is critical, miniature DC gearmotors have been developed. These tiny yet powerful motors are ideal for compact devices, such as medical equipment, drones, and precision instruments.
Conclusion
DC gearmotors are at the heart of countless devices and machines that we rely on daily. Their ability to convert electrical energy into mechanical movement with the right balance of speed and torque makes them invaluable in various industries. Whether it’s a robot, a fan, or an electric vehicle, DC gearmotors provide the power and precision needed to drive innovation in modern technology.
Understanding how these motors work and what factors to consider when choosing one for your project is crucial for ensuring success. With their growing range of applications, ongoing innovations, and relatively low cost, DC gearmotors will continue to be a fundamental component in the advancement of automation, robotics, and consumer electronics for years to come.
Established in 2005, Kpower has been dedicated to a professional compact motion unit manufacturer, headquartered in Dongguan, Guangdong Province, China.




































