In the realm of modern machinery and transportation, the quest for greater efficiency, power, and durability has driven engineers to innovate constantly. One such innovation that has quietly revolutionized industries is the integration of gas motors with gear reduction systems. These engineered marvels combine the raw energy of internal combustion engines with the mechanical finesse of gear assemblies, giving users a powerful yet controlled propulsion system.
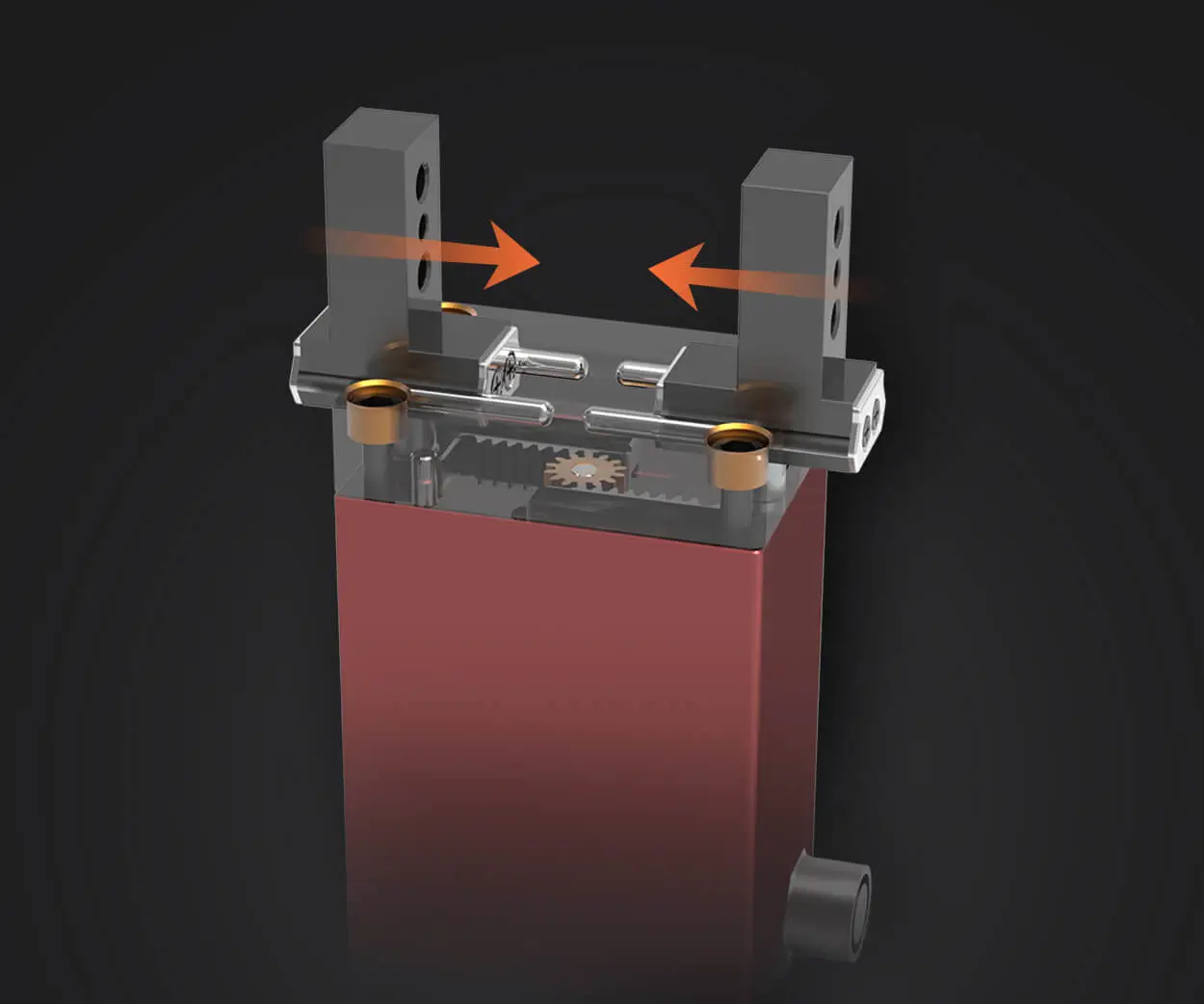
A gas motor, often referenced as an internal combustion engine, is designed to convert fuel into mechanical energy through controlled explosions within cylinders. It has been the backbone of transportation—from automobiles to boats—and industrial machinery. However, the raw power generated by a typical gas motor isn’t always suited for direct application, especially when precise control, high torque at low speeds, or energy efficiency are priorities.
That’s where gear reduction technology comes into play. Gear reduction involves attaching a set of gears—such as a gearbox or gear train—to the engine’s drive shaft. This gear assembly reduces the output speed of the motor while proportionally increasing torque. At first glance, this might seem counterintuitive—reducing speed to increase power—but in real-world applications, it’s a game changer. It allows a gas motor to operate at its optimal speed range, where it can generate maximum efficiency, while delivering the desired output torque and speed for specific tasks.
This synergy between a gas motor and gear reduction offers numerous advantages. For starters, it significantly amplifies the engine’s power output without needing to increase its size or fuel consumption dramatically. For example, in a small boat, a gas motor paired with a gear reduction system can propel the vessel efficiently, providing enough torque to cut through ripples without overworking the engine. The controlled, reduced rotational speed minimizes wear and tear, leading to longer engine life, and makes the entire system more fuel-efficient.
Furthermore, gear reduction systems permit fine-tuning of performance parameters. Different gear ratios can be selected based on operational needs. For instance, a larger gear ratio means more torque at the expense of speed, ideal for heavy-duty applications such as hauling or towing. Conversely, a smaller ratio favors higher speed, suitable for faster vehicles and equipment.
Understanding the mechanics of gear reduction in conjunction with gas motors requires a glance at gear types and arrangements. Spur gears, planetary gears, and helical gears are common choices. Each has its strengths and application fit. Spur gears are straightforward and cost-effective, often used for simple drive systems. Planetary gears are more complex but offer high torque density in compact configurations, making them popular in specialized machinery. Helical gears provide smoother operation and are suited for high torque scenarios where noise reduction is desired.
The integration process also involves selecting appropriate gear ratios. A ratio of 4:1, for instance, means the engine’s output shaft turns four times for each revolution of the gear’s output shaft. This effectively multiplies torque by four while reducing the output speed to a quarter. Precision in choosing the ratio is essential, as it influences performance, fuel consumption, and the lifespan of the system.
In addition to power and efficiency, safety and reliability are enhanced through the use of gear reduction. The gear system acts as a buffer, absorbing shocks and jolts that might otherwise compromise the engine or drivetrain. Properly lubricated gearboxes also minimize friction, reducing heat buildup and preventing overheating.
Industrial applications of gas motors with gear reduction are vast. They serve as the heart of generators, agricultural machinery, construction equipment, and even some recreational vehicles. Their modular design allows easy maintenance and customization, tailored to unique operational demands.
The evolution of gear reduction technology has paralleled advances in engine design and materials science. Today’s gearboxes feature precision machining, high-strength alloys, and advanced lubrication, which extend operational life and improve efficiency. Coupled with modern fuel injection and electronic controls, gas motors with gear reduction are more capable than ever.
Despite these technological strides, selecting the right combination remains a nuanced decision. Engineers consider factors such as power requirements, environmental conditions, maintenance capacity, and cost constraints. Often, the adjustments in gear ratios and gear types are optimally aligned with the specific use case—be it a small ATV needing high torque at low speeds or a high-speed boat requiring maximum efficiency at higher RPMs.
In sum, gas motors paired with gear reduction embody an elegant dance of physics and engineering that harmonizes raw power with practical usability. They symbolize progress towards smarter, more efficient, and more durable machinery. Now, let’s delve deeper into how these systems are implemented across various industries and explore some pioneering innovations shaping their future.
Leveraging innovations in modular drive technology, Kpower integrates high-performance motors, precision reducers, and multi-protocol control systems to provide efficient and customized smart drive system solutions.




































