Certainly! Here is the first part of the soft article based on the theme "DC Gear Motor 24V Torque":
part 1:
Imagine a world where machines move with precision, reliability, and efficiency — powered by tiny but mighty motors that turn dreams into reality. Among these marvels, the 24V DC gear motor stands out as a versatile workhorse, masterfully combining power and control to meet a vast array of industrial, commercial, and hobbyist needs.
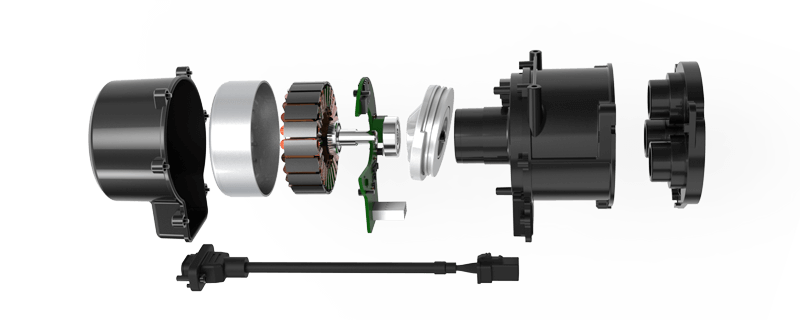
The essence of a DC gear motor
At its core, a DC gear motor is a simple yet powerful device consisting of a direct current (DC) motor coupled with a gear reducer. The DC motor converts electrical energy into rotational motion, while the gear reducer diminishes the motor's high speed and low torque into a lower speed and significantly higher torque output. Think of it as a perfect team: the motor provides quick, responsive motion, while the gear assembly amplifies that motion into torque-rich, controlled power.
The choice of 24 volts as the operating voltage adds a layer of robustness. It’s a sweet spot—high enough to deliver substantial torque and power without demanding overly complex power supplies or safety concerns associated with higher voltages. This makes 24V DC gear motors appealing for applications requiring reliable, steady performance without excessive complexity.
Understanding torque and its importance
Torque, the rotational equivalent of linear force, is the lifeblood of gear motors. It determines a motor’s ability to turn or lift heavy loads, accelerate objects, or maintain motion under resistance. When selecting a 24V DC gear motor, understanding torque specifications isn’t just a technical detail; it’s the key to ensuring your machine performs as intended.
The torque of a motor is typically expressed in Newton-meters (Nm) or ounce-inches, and it depends on several factors, including the motor's design, winding, and, critically, the gear ratio. The gear ratio—how many times the gear reducer turns for each motor revolution—directly influences torque amplification. For example, a 10:1 gear ratio can multiply the motor's base torque tenfold, allowing the motor to handle heavier loads or generate stronger force.
Why torque matters: real-world scenarios
Suppose you’re designing an automated conveyor system. The motor must not only spin the conveyor belt but also overcome the static friction of goods and the inertia of moving items. Here, a 24V DC gear motor with a high torque rating ensures smooth, steady operation, reduces motor strain, and prolongs lifespan.
Similarly, in robotics, torque determines a robot arm’s strength to lift objects or perform precise manipulations. A 24V gear motor providing ample torque ensures your robot can handle robust tasks without stalling or overheating. The importance of selecting the right torque value cannot be overstated because underpowered motors lead to sluggish performance and potential damage, while overly powerful motors increase costs and complicate control systems.
Efficiency and control
Matching the motor’s torque capacity with application demands is a balancing act. An over-torque scenario wastes energy and can cause unnecessary wear, while under-torquing risks stalled motion and operational failure. Modern 24V DC gear motors come with sophisticated control options, including gear ratio adjustments, speed controllers, and feedback systems, allowing fine-tuning of torque and speed according to specific needs.
Types of gear materials and their influence on torque
Gear reduction units typically use materials like plastic, aluminum, or steel. The choice impacts not just durability but also torque characteristics. Steel gears excel in high-torque applications due to their strength, making them suitable for heavy-duty machinery, whereas plastic gears offer quieter operation and are suited for lighter tasks.
The significance of gear ratio in torque output
Gear ratios can range from modest (e.g., 3:1) to high (e.g., 100:1 or more). Higher ratios produce greater torque but at the expense of speed. For instance, a 24V DC gear motor with a 50:1 gear ratio might deliver enough torque to lift heavy loads in industrial automation, but at a significantly reduced rotational speed—sometimes as low as a few revolutions per minute.
Emerging trends and innovative designs
The evolving landscape of 24V DC gear motors incorporates features like magnetic encoders for precise torque feedback, advanced gear materials for longer lifespan, and integrated motor controllers for seamless speed and torque adjustments. These innovations allow engineers and hobbyists alike to harness optimized torque characteristics for their bespoke applications, be it lightweight robotics or hefty industrial machinery.
Established in 2005, Kpower has been dedicated to a professional compact motion unit manufacturer, headquartered in Dongguan, Guangdong Province, China.




































