Sure! Here's the first part of the soft article based on the theme "AC and DC Servo Motor."
Unlocking the Power of Precision: An In-Depth Look at AC and DC Servo Motors
The pulse of modern industry beats heavily on the shoulders of precise, reliable motion control solutions. Among these, servo motors stand out as the heartbeat of automation systems, robotics, CNC machinery, and even aerospace advancements. They transform electrical energy into controlled mechanical movement, combining speed, torque, and positional accuracy—all in a compact package. But not all servo motors are created equal. When delving into the intricate world of servo technology, two giants dominate the scene: AC servo motors and DC servo motors. Understanding their differences, strengths, and weaknesses is paramount for selecting the right solution for your demanding application.
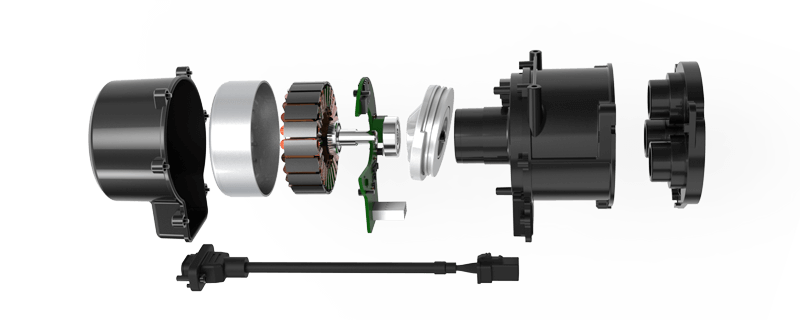
A Brief Introduction to Servo Motors
Before dissecting the differences, it’s worth reviewing what makes a servo motor special. Unlike standard motors, servo motors are paired with feedback devices such as encoders or resolvers that provide real-time data on position, velocity, and torque. This closed-loop system allows for remarkable precision and rapid adjustments, ensuring that the motor's output aligns perfectly with the commands.
Servo systems are used across diverse sectors—from high-speed robotic arms to precision manufacturing, from aerospace instruments to medical devices. The core advantage lies in their ability to deliver high torque at high speeds, maintain positional accuracy, and facilitate complex motion profiles with minimal error.
The Two Main Categories: AC and DC Servo Motors
The distinction between AC and DC servo motors lies primarily in their power sources and operational principles. While both serve similar roles, their internal designs and control methods differ significantly, influencing their suitability for specific applications.
DC Servo Motors: Stability and Precision
DC servo motors have been historically favored for their straightforward control mechanism and excellent low-speed torque capabilities. They operate on direct current, typically supplied by batteries or regulated power supplies. The key components include:
Armature winding, which creates the magnetic field Commutator and brushes, enabling electrical contact with the rotating armature
This design allows for precise control of speed and torque through adjusting the voltage and current supplied to the motor.
Advantages of DC Servo Motors:
Excellent Speed Control: The motor's speed can be adjusted smoothly over a wide range by varying the applied voltage or current. High Starting Torque: DC motors provide high torque at zero or low speeds, making them suitable for applications requiring strong, immediate force. Simple Control Systems: Their operational logic is relatively easy to understand and implement with basic electronics.
Limitations of DC Servo Motors:
Maintenance: The brushes and commutators wear out over time, requiring periodic replacement. Size and Complexity: Generally larger and heavier compared to equivalent AC motors. Limited Speed Range: At very high speeds, commutator and brush wear become problematic.
Part 2 will build further upon the properties of AC servo motors, their operational mechanisms, and real-world applications, providing a comprehensive comparison to help you determine the best fit for your needs.
Established in 2005, Kpower has been dedicated to a professional compact motion unit manufacturer, headquartered in Dongguan, Guangdong Province, China.




































