Understanding Servo Motors and Their Wiring Essentials
Servo motors are pivotal in robotics, automation, and various mechanical systems, known for their high precision and accurate control. These motors work based on a feedback loop that enables them to adjust and hold positions accurately, making them ideal for applications where fine movement is required. Whether you’re assembling a robotic arm, a drone, or a CNC machine, getting the servo motor wiring right is crucial to ensuring optimal performance.
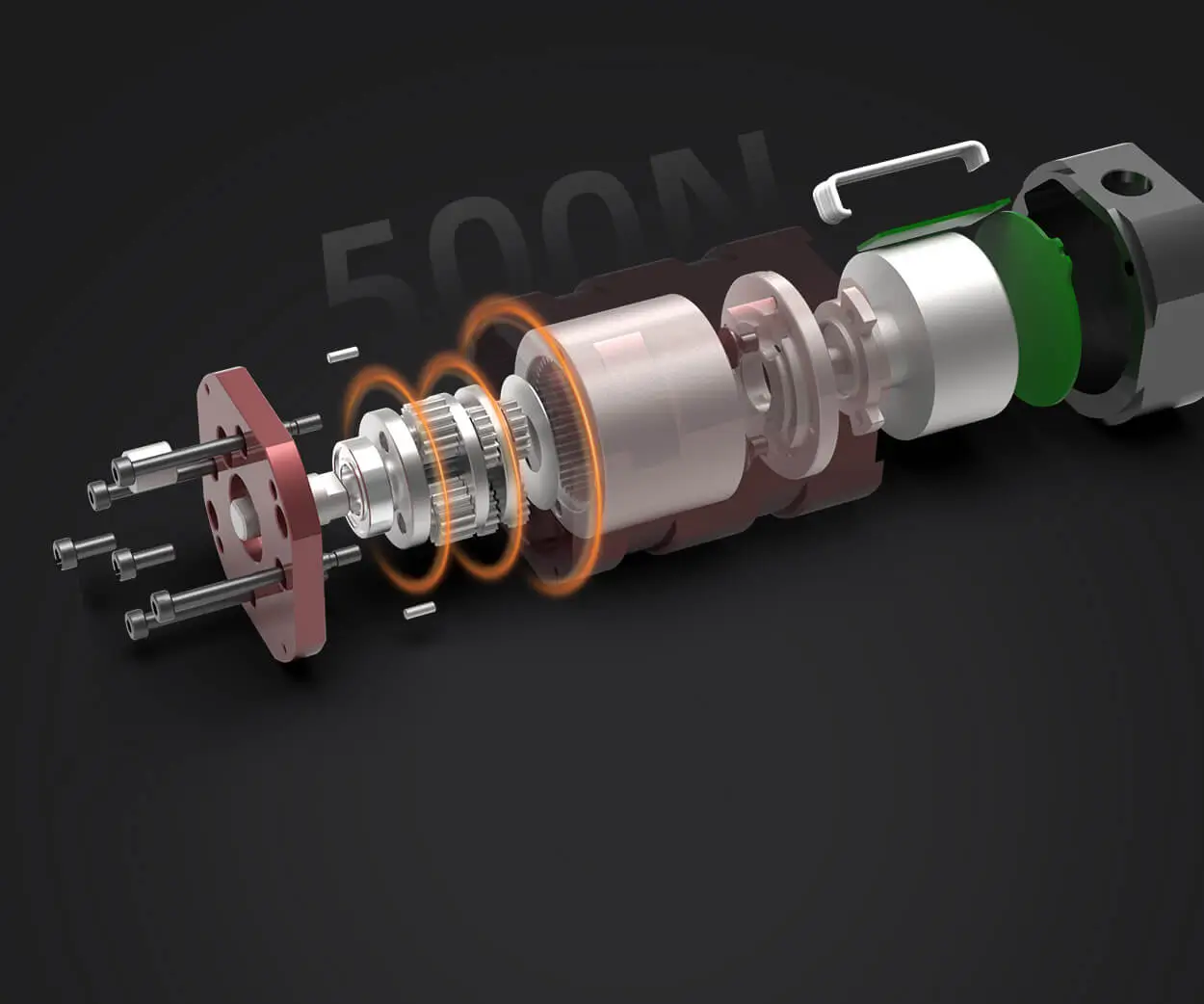
What is a Servo Motor?
A servo motor is a small, high-torque motor that can rotate to specific positions, based on the input signals it receives. Unlike regular motors, which rotate continuously, servo motors have built-in feedback control, allowing them to stop and hold at any given position.
Servo motors typically consist of:
Motor: The component that rotates.
Gearbox: Often a set of gears that amplifies the motor’s torque, ensuring precision.
Control Circuit: The system that reads feedback from the motor and adjusts the input signal to achieve the desired position.
Understanding these parts is essential when you’re setting up servo motor wiring since the connections you make will directly influence the motor's ability to respond to commands and hold its position.
Types of Servo Motors
Before diving into the wiring specifics, it's essential to understand the different types of servo motors available:
AC Servo Motors - These are used in high-torque applications where precision is paramount.
DC Servo Motors - These are often used in hobbyist projects and consumer products, offering easier control mechanisms.
Digital Servo Motors - These feature more advanced control systems and are commonly used in robotics and automation.
Analog Servo Motors - The more basic type, with a simpler control system.
Each type of servo motor may have slightly different wiring requirements, so knowing which one you're working with will help you determine the correct wiring method.
Components of Servo Motor Wiring
The wiring of a servo motor is quite straightforward but requires attention to detail. Generally, servo motors come with three wires:
Power (V+): This is typically the red wire and supplies the motor with the required power (usually between 4.8V to 6V for standard servos).
Ground (GND): This is the black or brown wire and connects the motor to the ground of the power supply.
Signal (PWM): This is the white or yellow wire, which carries the Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) signal to control the servo’s position.
Preparing the Power Supply
Before connecting the servo motor, you need to ensure that your power supply is capable of delivering the required voltage and current for the motor. Using a power supply with an inadequate current rating may result in the motor underperforming or, worse, damaging the motor or control circuit.
The voltage ratings for servos can vary, so refer to the datasheet of the specific servo you are using. For example, a typical 9g servo often works at 4.8V-6V, while larger, more industrial-grade motors might require higher voltages.
Establishing Ground Connections
Proper grounding is crucial in servo motor wiring. If the ground wire is not properly connected, you might experience erratic behavior or a failure in motor control. The ground of the power supply should be connected directly to the ground of the controller (usually a microcontroller or a receiver). Any grounding issues can cause noise or power instability in the control system, leading to poor performance.
Signal Wire Connection and PWM Control
The signal wire of the servo motor controls the motor’s position. This wire is typically controlled by a microcontroller, such as an Arduino, Raspberry Pi, or a specialized servo controller. The controller generates a PWM signal, which tells the servo how far to rotate. The pulse width (the duration of the high signal in the cycle) determines the motor’s position.
For example, a pulse width of 1.5 milliseconds might correspond to the neutral position (centered), while shorter or longer pulse widths (e.g., 1ms or 2ms) will move the servo to its extreme positions.
To wire the signal:
The signal pin from your controller goes to the signal pin of the servo motor.
Make sure the ground from your controller and the power supply are connected to avoid issues with the PWM signal interpretation.
Once you've connected all components, it's time to test the system by providing PWM signals and checking if the motor moves as expected.
Advanced Tips for Successful Servo Motor Wiring and Troubleshooting
Successfully wiring a servo motor involves more than just connecting a few wires. To ensure you maximize the efficiency, longevity, and precision of your setup, here are some advanced tips and troubleshooting strategies to consider.
Using Multiple Servos Together
In projects involving multiple servos, such as robotic arms or multi-jointed systems, you’ll need to wire each servo to its own signal output from your controller. While it's possible to use a single power supply to run multiple servos, ensure that the total current draw does not exceed the power supply’s capacity.
It’s also important to ensure that each servo has its own unique control signal (PWM), as servos must be driven independently to achieve precise movements. If you're using a microcontroller like Arduino, ensure that the PWM pins you use support the required signal output.
For better management of multiple servos, you might want to use a servo driver board or a servo controller. These devices can help manage the current and PWM signals more efficiently, especially when you're dealing with many servos.
Considerations for High Torque and Large Servos
For high-torque servos or industrial-grade motors, the wiring setup can get a bit more complex. Large servo motors might require separate power circuits and higher-current cables to ensure they perform optimally without overheating or causing voltage drops. In these setups, you’ll want to focus on:
Thicker wires for power lines to reduce resistance.
Separate power sources to prevent voltage dips.
Capacitors for smoothing out power fluctuations.
Additionally, it’s advisable to use servo extension cables that are rated for higher currents if you're dealing with larger motors.
Troubleshooting Common Servo Motor Wiring Issues
When your servo motor isn’t working as expected, the first step is always to check the wiring. Here are a few common issues and their solutions:
Motor Not Responding:
Check your power supply: Ensure the voltage is correct and the current capacity matches your servo’s requirements.
Signal issues: Confirm that your PWM signal is within the required frequency range for the servo, and make sure it’s being sent correctly from the controller.
Loose connections: Double-check all wire connections to ensure they are secure.
Erratic Behavior or Jittering:
This could be caused by poor power delivery. Servos require stable voltage, so consider adding capacitors to stabilize the power supply.
Also, check for issues with grounding; improper grounding can introduce noise that disrupts the signal.
Servo Moving Too Slowly or Too Fast:
This could indicate that the PWM signal’s frequency or pulse width isn’t set correctly. Recheck the specifications for the servo and ensure you’re sending the correct pulse width for your desired motion.
Servo Stalling:
If the servo motor stalls, it could be due to insufficient current from the power supply, too much load on the motor, or excessive resistance in the motor’s path. Ensure that the motor’s torque rating matches the mechanical load.
Final Tips for Successful Servo Motor Wiring
Read the manual: Always refer to the datasheet or manual for your servo. This will provide vital information such as recommended voltage, current, and PWM signal specifications.
Use quality components: Avoid cheap wires or low-quality connectors. Using proper wiring, resistors, and controllers will ensure reliable operation.
Safety first: When working with electricity, always disconnect the power before making adjustments to the wiring.
Mastering servo motor wiring is a valuable skill that will improve your work in robotics, automation, and other precision applications. With careful planning, attention to detail, and troubleshooting skills, you can ensure that your servo motors operate smoothly and efficiently every time.
Established in 2005, Kpower has been dedicated to a professional compact motion unit manufacturer, headquartered in Dongguan, Guangdong Province, China.




































